Introduction:
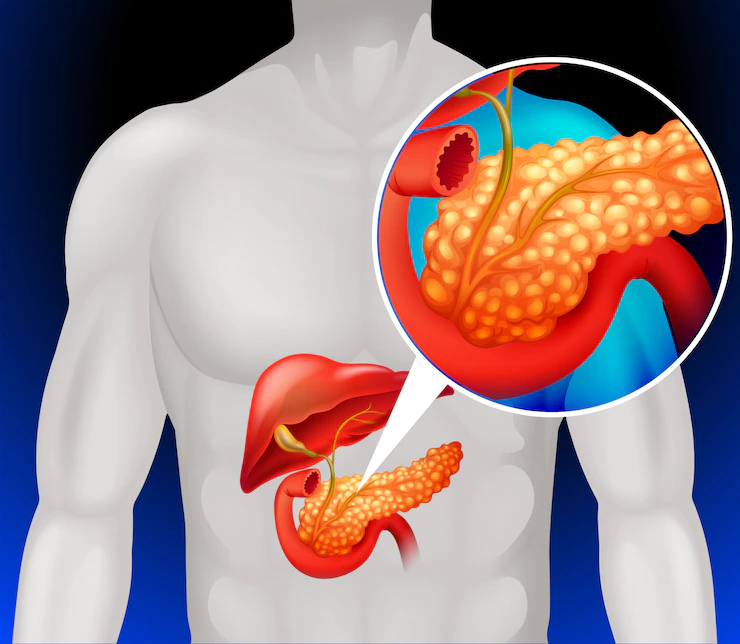
The pancreas is a tiny gland behind the stomach that looks like a hockey stick. Mutations in the pancreatic cells lead to their uncontrolled multiplication, resulting in pancreatic cancer forming a mass of tissue. This tumor is sometimes benign (not cancerous). Early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer is difficult because the pancreas is located deep within the body, and early tumors cannot be seen or felt during standard physical examinations. Symptoms normally do not appear until cancer has spread to other organs or has grown quite large.
Table of content:
- Types of pancreatic cancer
- Test for pancreatic cancer
- pancreatic cancer treatment
- pancreatic cancer treatment options
- pancreas surgery
- best pancreatic cancer treatment in Delhi
The main functions of pancreas include supporting food digestion and regulating blood sugar levels in the body. The pancreas helps in blood sugar regulation with the help of two hormones, insulin, and glucagon. Pancreatic cancer tends to spread to adjacent lymph nodes, then to the liver, peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity), and lungs if not diagnosed early.
Exocrine and neuroendocrine tumors are the two types of pancreatic cancer tumors that form in the pancreas. Exocrine tumors account for over 93% of all pancreatic tumors, and adenocarcinoma is the most frequent kind of pancreatic cancer. When people are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, it usually mean pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The most frequent kind is ductal adenocarcinoma, which starts in the pancreatic ducts.
The other 7% of pancreatic cancers are neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), also known as pancreatic NETs (PNETs), islet cell tumors, or islet cell carcinoma. Excess hormones are produced by some NETs. Insulinoma is a tumor in which excessive insulin is produced.
When someone visits the doctor after weeks or months of symptoms, they are frequently diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. Abdominal pain, weight loss, itching, and jaundice are common symptoms of pancreatic cancer.
The lifetime risk of pancreatic cancer is approximately 1 in 64. A risk factor is something that increases your chances of contracting an illness. There are risk variables that are caused by behavior and lifestyle. These are some of the risk factors for pancreatic cancer:
- Smoking cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products.
- Obesity is a risk factor as well. Even if you are not obese, carrying excess weight around your waist is a dangerous factor.
- Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, is associated with obesity. The onset of diabetes at an older age in someone who has a healthy weight and BMI could be a symptom of pancreatic cancer.
- Experiencing chemical exposure
Test for pancreatic cancer
To understand more about your symptoms, your doctor will inquire about your medical history. The doctor may also inquire about potential risk factors such as smoking and family history. He will evaluate you for signs of pancreatic cancer or other health issues. Pancreatic tumors can cause the liver or gallbladder to expand, which may be detected during the exam. Jaundice will be checked on your skin and the whites of your eyes (yellowing).
If the physical results are odd, your doctor will most likely order tests to assist identify the problem. Further tests and therapy may be recommended by a gastroenterologist (a doctor who specializes in digestive system diseases).
A doctor may prescribe a few diagnostic tests for pancreatic cancer like an imaging test, blood test, biopsies based on a person’s checkup, lab tests, and symptoms description.
- A computer recreates several X-ray images into detailed images of the inside of the abdomen using computed tomography (CT scan). A CT scan aids in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) generates comprehensive images of the abdomen using magnetic waves, particularly around the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder.
- Ultrasound: Non-harmful sound waves reflected back from the organs in the abdomen produce images that could aid doctors in diagnosing pancreatic cancer.
- PET scan (positron emission tomography): PET scans may aid in determining the extent to which pancreatic cancer has spread around the surrounding organs.
- Blood test: Blood Investigations for liver function tests and tumor markers are done to screen the carcinogen in the body.
A pancreatic cancer diagnosis is likely but not certain if imaging investigations reveal a mass in the pancreas. Pancreatic cancer can only be diagnosed with a biopsy, which involves extracting real tissue from the tumor. Biopsies can be done via
- Percutaneous needle biopsy: A radiologist inserts a needle into the mass under imaging guidance, collecting some tissue. Fine needle aspiration is another name for this operation (FNA).
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and other equipment through the mouth into the small intestine near the pancreas. ERCP can obtain photos of the area as well as a tiny biopsy using a brush.
- Endoscopic ultrasound: An endoscope is put near the pancreas, similar to ERCP. The mass is located using an ultrasonic probe on the endoscope, and tissue is extracted using a needle on the endoscope.
- Laparoscopy is a surgery that involves multiple tiny incisions. A surgeon can use laparoscopy to collect tissue for biopsy and examine inside the abdomen to see if pancreatic cancer has spread.
Pancreatic cancer treatment
When diagnosis of pancreatic cancer is done at an advanced stage, treatment of pancreatic cancer becomes difficult.
The pancreatic cancer treatment option is determined by several factors, including the location of the tumor, its stage, your overall health, and whether the disease has progressed beyond the pancreas.
Pancreatic cancer Treatment option includes:
Surgical Method: The malignant part of the pancreas is removed surgically (resection). It’s also possible to remove lymph nodes around the pancreas.
- A pancreatectomy is a procedure that removes the pancreas or a portion of the pancreas. If your tumor is at the head of the pancreas (the broadest section of the pancreas near the small intestine), your doctor may consider the Whipple procedure. The head of the pancreas, the duodenum (the first piece of the small intestine), the gallbladder, and a portion of the bile duct are all removed during this surgery.
- Radiation therapy is the use of high-speed energy to eliminate cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: It is a treatment that employs chemicals to kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: It is a treatment that assists your body in fighting cancer. Immunotherapy has been mainly ineffective against pancreatic cancer, however, it may help roughly 1% of people with the disease and a certain genetic mutation.
- Targeted therapy: It is directed at certain genes or proteins that aid in the growth of cancer. A genetic testing is generally used to see if a tailored therapy is good for you.
Before Pancreatic surgery, chemotherapy and/or radiation may be used to reduce the size of the tumor to ensure that all cancer cells are eliminated following surgery. Before the Pancreas Surgery is scheduled you should feel comfortable discussing pancreatic cancer treatment options with your healthcare team.
You and your doctor should also talk about how to avoid or minimize the negative effects of your treatment. Supportive or palliative care may include the activities:
- Pain Management: To reduce the pain if medications failed.
- Treatment for jaundice: Your healthcare practitioner may place a stent (tube) inside your bile duct to relieve your symptoms.
- Reduced intestinal obstruction: A stent can be inserted to open up a blockage in your small intestine.
- Controlling Diabetes: Your medical team can assist you in monitoring your blood sugar levels and managing your diabetic medication.
- Supportive care can also assist you in understanding and processing your feelings, as well as those of your family and friends.
Best Pancreatic cancer treatment is available in Delhi NCR. The well-known distinguished gastroenterologist has come a long way in providing complete and comprehensive cancer treatment to patients from India and across the world. He is a liver specialist who specializes in therapeutic endoscopy and ERCP. He is an expert in procedures such as colonoscopy, endoscopy, ERCP, sigmoidoscopy, ultrasound, and capsule endoscopy, and also in the treatment of gastrointestinal issues and liver diseases. His versatile knowledge backed with years of experience makes him the most acknowledged surgeon in the field of gastroenterology, focusing on quality, care, and innovation. He along with his team ensures that every patient receives the best diagnosis and treatment. Every patient who comes to his clinic is initially diagnosed using the relevant tests. The goal of diagnosis is to determine the root cause of the medical illness or condition, diagnose it, and offer the best treatment possible.
Takeaway:
When uncontrolled cell growth occurs in a region of the pancreas, pancreatic cancer develops. Jaundice and stomach pain are major symptoms that may not develop until later stages. Early diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer is challenging, making its treatment and prevention more difficult. Certain checks and tests are performed to determine the cause of signs and symptoms that could be caused by pancreatic cancer. If cancer is diagnosed, more investigations are done to evaluate cancer’s extent (stage) and to plan the treatment.