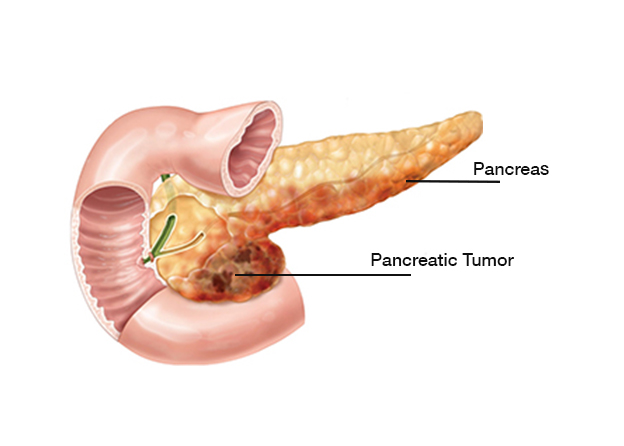
The pancreas, located in the abdomen, has cells with endocrine (hormonal) and exocrine (digestive) functions; cancer cells can develop from both types of functional cells. Pancreatic cancer strikes a small organ behind the stomach that produces hormones and digestive juices for the body. Pancreatic cancer occurs within the tissues of the pancreas, which is a vital endocrine organ located behind the stomach.
Pancreatic cancer that spreads may worsen pre existing symptoms. If cancer spreads, you may experience additional signs and symptoms of advanced pancreatic cancer. The cause of pancreatic cancer is unknown. This type of cancer occurs when irregular cells start to grow within the pancreas and make tumors.
Usually, healthy cells grow and die in reasonable quantities. In cancer, there is an increased amount of abnormal cell production, and these cells eventually take over healthy cells.
According to Gastroenterologist in Delhi Pancreatic cancer often doesn’t show symptoms until it reaches the advanced stages of the disease.
Therapy for pancreatic cancer treatment in delhi depends on the stage of growth. It has two goals: to kill cancerous cells and to prevent the spread of the disease